Bitcoin: Local regulations’ impact on price ‘short-lived’

As the crypto-space inches closer to achieving infrastructural development, the world has been looking at it closely. Even though regulators around the world have been skeptical about Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, the regulation of digital assets has been looked upon as a necessary action. A framework around cryptos will instill trust among users, thus promoting adoption. However, is the crypto market equipped to adapt to the regulatory changes that will come?
A recent research paper by the Asian Development Bank Economics on Global Bitcoin Markets and Local Regulations, elaborated on the effect of government regulations on the price of Bitcoin and related trading activities. The research focused on the six Bitcoin trading markets – USD, Euro, Yen, Yuan, Won, and Pound Sterling, that comprised of 99% of the global trading volume, as of February 2018.
Even though local regulations seemed like the way to go, the report noted that an effort by national regulators to collaborate for a harmonized approach across jurisdictions could help in fostering the healthy development of the crypto-market.
After studying the regulations issued by the six major BTC markets from April 2013 to February 2018, it was found that the issuance of local market regulations resulted in the Bitcoin prices dropping in the short-term. However, from the third day onwards, the abnormal price pattern disappeared, meaning, the impact of local market regulations on the price of Bitcoin was only short-lived. Despite having a small impact on BTC’s price, the price of the digital assets differed considerably across individual national markets.
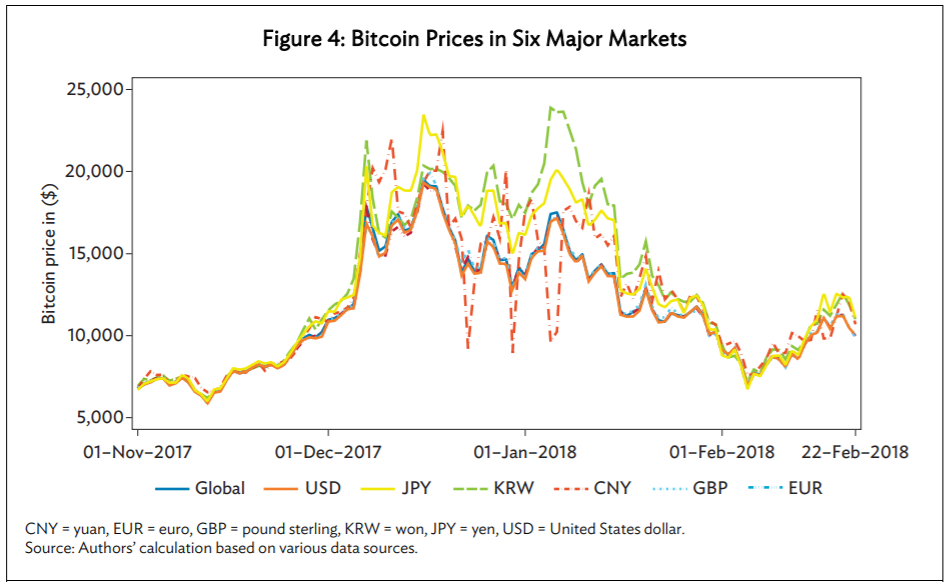
Source: ADB Economics
Apart from the price impact, the data collated found that these local regulations played a role in discouraging trading activities. Further, the study said that regulation events saw an abnormal increase in the trading volume for the first two days, however, they declined soon after, for 10 straight days in the local market. This indicated that investors initially trade even more actively to adjust their positions in the local market, in response to regulations.
However, the restricted trading cannot be reverted and presented itself as a lasting repressive impact on trading in local markets.
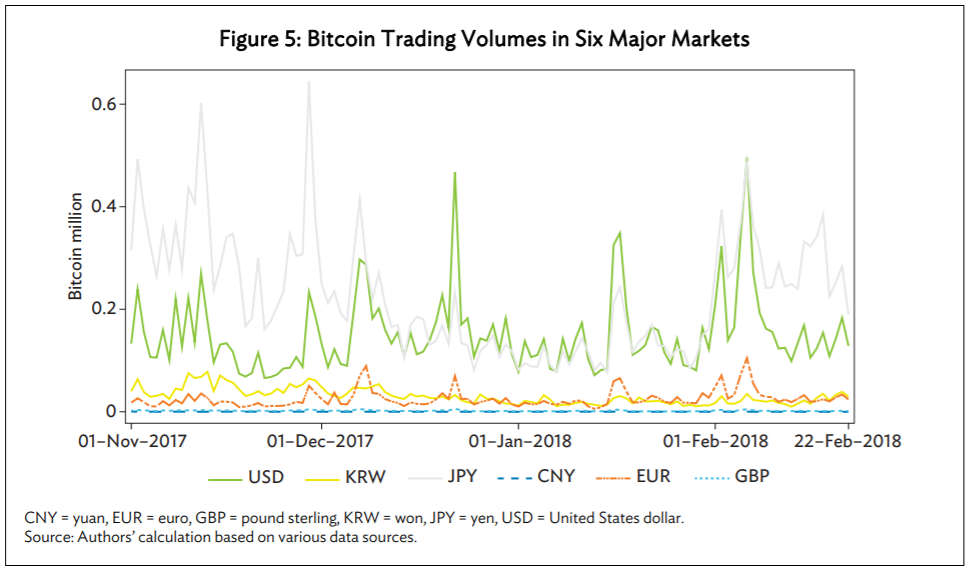
Source: ADB Economics
Thus, it can be observed that the global Bitcoin price is globally determined and cannot be influenced by individual markets. The paper’s findings also implied that the global BTC market is highly integrated and local price variations are due to market frictions associated with foreign exchange markets, and not the segmentation of the local BTC market.